mump2p Protocol
mump2p is a next-generation gossip protocol that uses Random Linear Network Coding (RLNC) to revolutionize message dissemination in peer-to-peer networks. Built on libp2p, it offers a high-performance alternative to traditional protocols like GossipSub, delivering faster propagation, better bandwidth efficiency, and better fault tolerance using network coding.
How mump2p Works
mump2p is a gossip mechanism based on RLNC, also known as Galois Gossip, that builds upon libp2p's GossipSub protocol. Instead of transmitting complete messages between peers, mump2p breaks messages into coded shards that can be independently forwarded and mathematically recombined to reconstruct the original data.
Node Architecture
Each mump2p node is a standard libp2p host enhanced with RLNC logic. Core components include:
- libp2p Host – Provides peer discovery, secure communication, and network transport.
- Mesh Topology – Maintains a configurable gossip mesh with peer degrees similar to GossipSub.
- RLNC – Manages encoding, recoding, and decoding of shards based on tunable parameters.
See Configuration Parameters for details.
Random Linear Network Coding (RLNC) Fundamentals
RLNC enables performance gains by dividing messages into linearly coded shards. These shards can be forwarded, recombined, and decoded efficiently without requiring complete message delivery.
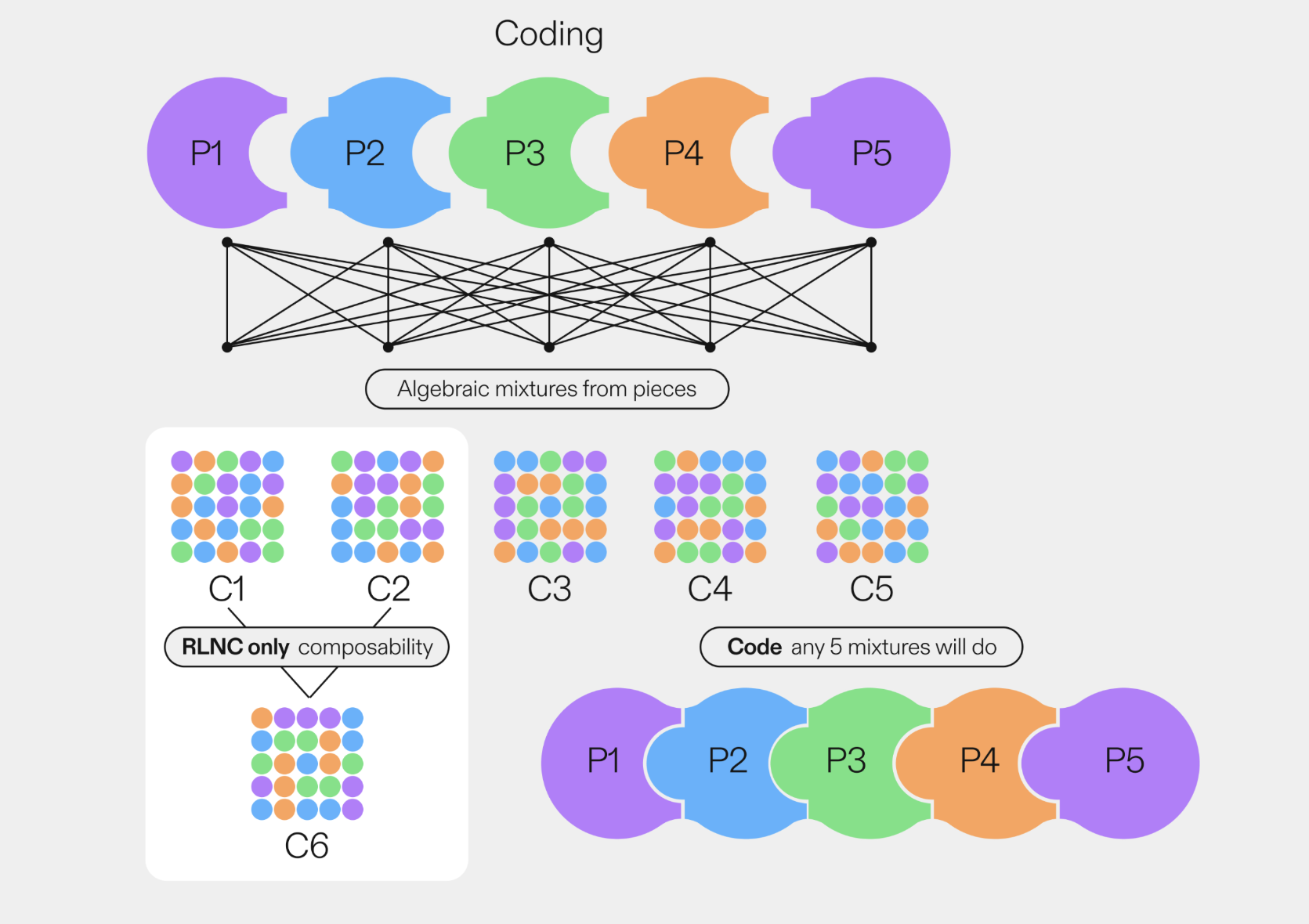
Key Concepts
- Encoding: The original message is split into
kfragments. These are used to producencoded shards via random linear combinations over a finite field, ensuring uniqueness and redundancy. - Recoding (Composability): Any node that receives a shard can immediately create a new coded shard from its current shard set — without waiting for the full message. This enables continuous, fast, and fault-tolerant propagation.
- Decoding: Nodes only need
klinearly independent shards to reconstruct the original message using linear algebra (matrix inversion). This ensures high resilience to data loss.
Benefits
- Lower Latency: Messages are broken into coded shards, which can be forwarded to the next node before the whole message is received.
- High Loss Tolerance: Messages can be decoded with any combination of shards, as long as a sufficient number reach the destination.
- Bandwidth Efficiency: Sharding and recoding reduce the amount of redundant data transmission, lowering overall bandwidth usage.
Protocol Operation
When Publishing
When a node receives a shard:
- Message Preparation: Add length prefix and pad if necessary.
- Encoding:
- Fragment the message using
ShredFactor - Generate coded shards:
num_shards = ShredFactor * PublisherShardMultiplier
- Fragment the message using
- Shard Distribution: Send different coded shards to different peers in round-robin fashion.
When Receiving a Shard
- Validation: Check for linear independence; discard redundant shards.
- Storage: Add to shard set for that message.
- Decoding: Attempt decoding once
kunique shards are available. - Forwarding:
From Publisher: Shards are immediately forwarded to all mesh peers.From Peers: If shard count exceedsForwardShardThreshold, generate and forward a recoded shard.
Control Messages
mump2p uses and extends GossipSub's control messages for optimized mesh performance:
| Message | Purpose |
|---|---|
IDONTWANT | Informs peers not to send more shards for a decoded message |
IHAVE | Advertises that a node holds coded shards for a message |
IWANT | Requests additional shards for an undecoded message |
GRAFT/PRUNE | Maintains optimal mesh size by adding/removing peers dynamically |
Configuration Parameters
mump2p provides several configurable parameters to tune performance for different network conditions and requirements:
RLNC Encoding
- ShredFactor: Number of base fragments to split a message into before encoding. Higher values provide more granular sharding but increase computational overhead.
- PublisherShardMultiplier: Determines how many coded shards to create initially when publishing a message. Formula:
coded_shards_created = ShredFactor * PublisherShardMultiplier. - ForwardShardThreshold: Sets the threshold for intermediate nodes to create and forward new recoded shards. Nodes forward when they have more than
ShredFactor * ForwardShardThresholdshards.
Mesh Topology Parameters
mump2p builds upon libp2p's GossipSub mesh topology, where peers maintain full-message peerings for reliable data transmission and metadata-only peerings for gossip and network maintenance.
- MeshDegreeTarget: Target number of peers to maintain in the mesh overlay. This controls the trade-off between speed, reliability, resilience and efficiency of the network. A higher peering degree helps messages get delivered faster with better reliability, but increases bandwidth usage due to redundant message copies.
- MeshDegreeMin: Minimum number of mesh peers before triggering grafting (converting metadata-only connections to full-message).
- MeshDegreeMax: Maximum number of mesh peers before triggering pruning (converting full-message peerings back to metadata-only).
In libp2p's default implementation, the ideal network peering degree is 6 with anywhere from 4–12 being acceptable. mump2p inherits these mesh management mechanisms while optimizing shard propagation through the established topology.
Use Cases
mump2p serves as a foundational, general-purpose data propagation protocol with benefits extending across various blockchain use cases.
Validators and Node Operators
mump2p supercharges validator and full node performance in bandwidth-constrained and latency-sensitive networks:
- Ethereum: Faster mempool propagation, lower uncle rates, and potential integration into both execution and consensus layers.
- Solana: Enhances Turbine-style data sharding with fault-tolerant packet loss recovery.
- Cosmos & IBC networks: Low-latency interchain packet routing and zone-to-zone messaging.
DeFi, AI, DePIN, Gaming & Social Chains
Security Model
mump2p inherits libp2p's robust security foundation, and adds safeguards specific to network coding.
Inherited from libp2p
- Authenticated and Encrypted Channels: All peer-to-peer communication is secured using Noise or TLS, preventing eavesdropping and tampering.
- Sybil and Eclipse Attack Mitigation: The protocol uses libp2p's peer discovery and management systems, which include defenses against an attacker flooding the network with malicious nodes to gain control or isolate honest peers.
For a full overview of these protections, refer to the libp2p security considerations.
mump2p avoids Pollution Attacks
In pollution attacks attack, a malicious actor injects corrupted or invalid coded shards into the network, with the goal of preventing honest nodes from successfully decoding the original message.
mump2p mitigates this risk through a multi-layered approach centered on source authentication.
- The original message data is cryptographically hashed to create a unique identifier.
- This identifier, along with the publisher's signature, is bound to the data.
- When a node decodes a message from a set of shards, it can verify the reconstructed data against the publisher's original signature and hash.
If the verification fails, the node knows that at least one of the shards it received was polluted. While identifying the exact malicious shard can be complex, the system can identify the peers who sent the invalid shards and lower their reputation scores, eventually isolating them from the network. This ensures that even though recoding happens at intermediate nodes, the integrity of the data can be verified end-to-end.

